
Electronics#ar #VR #AR Glasses #Augmented Reality #Virtual Reality #techtok #cftech
Use this section to provide a description of your blog./pages/blog
What specific encryption methods will be used in AI Glasses?
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
While specific encryption methods for AI glasses have not been universally defined, several established techniques are likely to be employed to enhance data security and privacy. Here are some commonly used encryption methods that could be relevant:
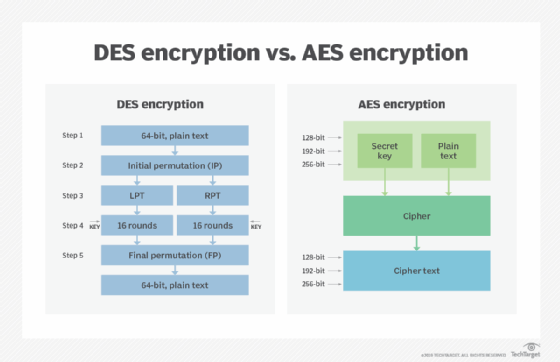
1. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- Description: A symmetric encryption algorithm widely used for securing data.
- Application: It can be used for encrypting stored data on the device and for secure communication between the glasses and other devices.
2. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
- Description: An asymmetric encryption algorithm that uses a pair of keys (public and private) for secure data transmission.
- Application: Useful for securely exchanging keys between devices or for signing data.
3. TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Description: A protocol that provides secure communication over a computer network.
- Application: Ensures that data transmitted between the AI glasses and cloud services or other devices is encrypted and secure from eavesdropping.
4. ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
- Description: A form of public key cryptography that offers similar security to RSA but with smaller key sizes, making it efficient for devices with limited processing power.
- Application: Suitable for establishing secure connections and authentication processes in AI glasses.
5. Hashing Algorithms (e.g., SHA-256)
- Description: Used to create a fixed-size hash value from input data, ensuring data integrity.
- Application: This can be used to verify the integrity of data being transmitted or stored, ensuring it hasn’t been altered.
6. End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
- Description: A method of data transmission where only the communicating users can read the messages.
- Application: Ensures that data sent from the AI glasses to another party is only accessible to the intended recipient.
7. Secure Multi-Party Computation
- Description: A technique that allows multiple parties to compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private.
- Application: Useful for collaborative applications where privacy is essential.
8. Homomorphic Encryption
- Description: Allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without needing to decrypt it first.
- Application: Could be useful for processing data in the cloud while maintaining user privacy.
By implementing a combination of these encryption methods, AI glasses can enhance their data security framework, protecting user information from unauthorized access and ensuring privacy during data transmission and storage.
Read more
While specific encryption methods for AI glasses have not been universally defined, several established techniques are likely to be employed to enhance data security and privacy. Here are some commonly used encryption methods that could be relevant:

1. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- Description: A symmetric encryption algorithm widely used for securing data.
- Application: It can be used for encrypting stored data on the device and for secure communication between the glasses and other devices.
2. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
- Description: An asymmetric encryption algorithm that uses a pair of keys (public and private) for secure data transmission.
- Application: Useful for securely exchanging keys between devices or for signing data.
3. TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Description: A protocol that provides secure communication over a computer network.
- Application: Ensures that data transmitted between the AI glasses and cloud services or other devices is encrypted and secure from eavesdropping.
4. ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
- Description: A form of public key cryptography that offers similar security to RSA but with smaller key sizes, making it efficient for devices with limited processing power.
- Application: Suitable for establishing secure connections and authentication processes in AI glasses.
5. Hashing Algorithms (e.g., SHA-256)
- Description: Used to create a fixed-size hash value from input data, ensuring data integrity.
- Application: This can be used to verify the integrity of data being transmitted or stored, ensuring it hasn’t been altered.
6. End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
- Description: A method of data transmission where only the communicating users can read the messages.
- Application: Ensures that data sent from the AI glasses to another party is only accessible to the intended recipient.
7. Secure Multi-Party Computation
- Description: A technique that allows multiple parties to compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private.
- Application: Useful for collaborative applications where privacy is essential.
8. Homomorphic Encryption
- Description: Allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without needing to decrypt it first.
- Application: Could be useful for processing data in the cloud while maintaining user privacy.
By implementing a combination of these encryption methods, AI glasses can enhance their data security framework, protecting user information from unauthorized access and ensuring privacy during data transmission and storage.
Read more
How will AI glasses address privacy concerns effectively?
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
Addressing privacy concerns with AI glasses will be critical for their acceptance and use. Here are some effective strategies that manufacturers and developers may implement:

1. User Control Over Data
- Opt-in Features: Allow users to choose what data is collected and shared.
- Data Management Tools: Provide easy-to-use settings for users to manage their privacy preferences.
2. Transparent Data Policies
- Clear Communication: Offer straightforward explanations of how data is used, stored, and shared.
- Regular Updates: Inform users about any changes in privacy policies or data handling practices.

3. Real-Time Notifications
- Indicator Lights: Use visual indicators (like LED lights) to show when recording or data collection is active, keeping users aware of their surroundings.
- Alerts for Data Sharing: Notify users when data is being shared with third parties.
4. Enhanced Security Measures
- End-to-End Encryption: Ensure that data transmitted to and from the glasses is encrypted to protect against unauthorized access.
- Secure Authentication: Implement robust authentication methods (e.g., biometrics, two-factor authentication) to prevent unauthorized use.
5. Privacy by Design
- Built-In Privacy Features: Design the hardware and software with privacy in mind from the outset, minimizing data collection where possible.
- Anonymous Data Processing: Techniques like anonymization or aggregation are used to protect individual identities in data analysis.
6. User Education
- Awareness Campaigns: Educate users about potential privacy risks and best practices for safe use.
- Guidance on Settings: Provide tutorials on how to configure privacy settings effectively.
7. Compliance with Regulations
- Adherence to Laws: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA, which set standards for user privacy rights.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of data practices to ensure compliance and transparency.
8. Community Feedback
- User Input: Engage with users to gather feedback on privacy concerns and desired features.
- Beta Testing: Involve users in beta testing phases to identify and address privacy issues before wide-scale release.
By implementing these strategies, manufacturers of AI glasses can address privacy concerns more effectively, fostering user trust and encouraging broader adoption.
Read more
Addressing privacy concerns with AI glasses will be critical for their acceptance and use. Here are some effective strategies that manufacturers and developers may implement:

1. User Control Over Data
- Opt-in Features: Allow users to choose what data is collected and shared.
- Data Management Tools: Provide easy-to-use settings for users to manage their privacy preferences.
2. Transparent Data Policies
- Clear Communication: Offer straightforward explanations of how data is used, stored, and shared.
- Regular Updates: Inform users about any changes in privacy policies or data handling practices.

3. Real-Time Notifications
- Indicator Lights: Use visual indicators (like LED lights) to show when recording or data collection is active, keeping users aware of their surroundings.
- Alerts for Data Sharing: Notify users when data is being shared with third parties.
4. Enhanced Security Measures
- End-to-End Encryption: Ensure that data transmitted to and from the glasses is encrypted to protect against unauthorized access.
- Secure Authentication: Implement robust authentication methods (e.g., biometrics, two-factor authentication) to prevent unauthorized use.
5. Privacy by Design
- Built-In Privacy Features: Design the hardware and software with privacy in mind from the outset, minimizing data collection where possible.
- Anonymous Data Processing: Techniques like anonymization or aggregation are used to protect individual identities in data analysis.
6. User Education
- Awareness Campaigns: Educate users about potential privacy risks and best practices for safe use.
- Guidance on Settings: Provide tutorials on how to configure privacy settings effectively.
7. Compliance with Regulations
- Adherence to Laws: Ensure compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA, which set standards for user privacy rights.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of data practices to ensure compliance and transparency.
8. Community Feedback
- User Input: Engage with users to gather feedback on privacy concerns and desired features.
- Beta Testing: Involve users in beta testing phases to identify and address privacy issues before wide-scale release.
By implementing these strategies, manufacturers of AI glasses can address privacy concerns more effectively, fostering user trust and encouraging broader adoption.
Read more
Microsoft HoloLens 3
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
The Microsoft HoloLens 3 is an advanced mixed-reality headset designed for various applications, particularly in enterprise and healthcare settings. Here are some key features and aspects of the device:

1. Enhanced Mixed Reality Experience
- Improved Field of View: This offers a wider field of view compared to its predecessors, allowing users to see more holographic content simultaneously.
- High-Resolution Displays: Features advanced display technology that enhances clarity and visual fidelity, providing a more immersive experience.
2. Robust Interaction Capabilities
- Hand Tracking: Supports natural hand gestures for interaction, allowing users to manipulate holograms intuitively.
- Eye Tracking: Incorporates eye tracking technology for more precise control and interaction, enhancing usability.
3. Advanced Audio Features
- Spatial Audio: Provides immersive sound experiences that align with the visual components, improving the overall engagement with holograms.
4. Enterprise-Grade Applications
- Healthcare: Used for surgical planning, training, and patient education, allowing for interactive visualizations and real-time collaboration.
- Manufacturing and Design: Facilitates design reviews, assembly processes, and training simulations, improving efficiency in industrial applications.
5. Collaboration Tools
- Remote Assistance: Enables remote collaboration, allowing experts to assist on-site workers through shared views and interactive annotations.
- Multi-User Experiences: Supports simultaneous use by multiple users, enhancing teamwork and collaborative tasks.
6. Durability and Comfort
- Ergonomic Design: Built for extended use, with adjustable features to ensure comfort during long sessions.
- Durable Construction: Designed to withstand the rigors of industrial environments.
7. Software Ecosystem
- Windows Mixed Reality: Runs on a version of Windows tailored for mixed reality applications, providing access to a range of software tools and development kits.
- Integration with Microsoft Services: Seamlessly integrates with Microsoft 365 and Azure, allowing for enhanced productivity and data management.
Conclusion
The HoloLens 3 represents a significant advancement in mixed reality technology, providing powerful tools for enterprises, particularly in the healthcare, manufacturing, and design sectors. Its enhanced features and capabilities make it a versatile platform for innovation and collaboration.
Read more
The Microsoft HoloLens 3 is an advanced mixed-reality headset designed for various applications, particularly in enterprise and healthcare settings. Here are some key features and aspects of the device:

1. Enhanced Mixed Reality Experience
- Improved Field of View: This offers a wider field of view compared to its predecessors, allowing users to see more holographic content simultaneously.
- High-Resolution Displays: Features advanced display technology that enhances clarity and visual fidelity, providing a more immersive experience.
2. Robust Interaction Capabilities
- Hand Tracking: Supports natural hand gestures for interaction, allowing users to manipulate holograms intuitively.
- Eye Tracking: Incorporates eye tracking technology for more precise control and interaction, enhancing usability.
3. Advanced Audio Features
- Spatial Audio: Provides immersive sound experiences that align with the visual components, improving the overall engagement with holograms.
4. Enterprise-Grade Applications
- Healthcare: Used for surgical planning, training, and patient education, allowing for interactive visualizations and real-time collaboration.
- Manufacturing and Design: Facilitates design reviews, assembly processes, and training simulations, improving efficiency in industrial applications.
5. Collaboration Tools
- Remote Assistance: Enables remote collaboration, allowing experts to assist on-site workers through shared views and interactive annotations.
- Multi-User Experiences: Supports simultaneous use by multiple users, enhancing teamwork and collaborative tasks.
6. Durability and Comfort
- Ergonomic Design: Built for extended use, with adjustable features to ensure comfort during long sessions.
- Durable Construction: Designed to withstand the rigors of industrial environments.
7. Software Ecosystem
- Windows Mixed Reality: Runs on a version of Windows tailored for mixed reality applications, providing access to a range of software tools and development kits.
- Integration with Microsoft Services: Seamlessly integrates with Microsoft 365 and Azure, allowing for enhanced productivity and data management.
Conclusion
The HoloLens 3 represents a significant advancement in mixed reality technology, providing powerful tools for enterprises, particularly in the healthcare, manufacturing, and design sectors. Its enhanced features and capabilities make it a versatile platform for innovation and collaboration.
Read more
What specific software features did Apple add to Vision Pro?
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
At CES 2025, Apple showcased several specific software features added to the Vision Pro that enhance its functionality and user experience. Here are the notable updates:
1. Enhanced Spatial Computing
- Feature: Improved spatial awareness capabilities that allow for more accurate placement of virtual objects in the physical environment.
- Benefit: Enables seamless interaction with digital content as if it were part of the real world.
2. Multi-User Support
- Feature: New multi-user functionality that allows multiple users to share the same AR space while maintaining individual profiles and experiences.
- Benefit: Enhances collaborative experiences, making it ideal for family use or team projects in professional settings.
3. Expanded App Ecosystem
- Feature: A broader range of apps optimized for the Vision Pro, including productivity tools, games, and creative applications.
- Benefit: Users can access a variety of applications tailored to take advantage of AR capabilities, enhancing overall utility.
4. Gesture and Voice Control Improvements
- Feature: Enhanced gesture recognition and voice command capabilities for more intuitive navigation and interaction.
- Benefit: Makes it easier to control apps and content without needing handheld controllers, providing a more immersive experience.
5. Integration with Apple Ecosystem
- Feature: Deeper integration with other Apple devices, such as iPhones, iPads, and Macs, allowing for seamless sharing of content and continuity across devices.
- Benefit: Enhances user convenience by enabling synchronized experiences and easy access to files and applications.
6. Customizable User Interface
- Feature: A more customizable user interface that allows users to arrange their digital workspace according to their preferences.
- Benefit: Provides a personalized experience, making it easier for users to access frequently used apps and tools.
7. Improved Privacy Settings
- Feature: Enhanced privacy features that allow users to control data sharing and manage permissions more effectively.
- Benefit: Increases user confidence in using the device by ensuring better data protection.
Conclusion
These software enhancements to the Apple Vision Pro underscore Apple's commitment to creating a versatile and user-friendly AR experience, blending digital content seamlessly with the physical world while providing powerful tools for collaboration and personalization.
Read more
At CES 2025, Apple showcased several specific software features added to the Vision Pro that enhance its functionality and user experience. Here are the notable updates:
1. Enhanced Spatial Computing
- Feature: Improved spatial awareness capabilities that allow for more accurate placement of virtual objects in the physical environment.
- Benefit: Enables seamless interaction with digital content as if it were part of the real world.
2. Multi-User Support
- Feature: New multi-user functionality that allows multiple users to share the same AR space while maintaining individual profiles and experiences.
- Benefit: Enhances collaborative experiences, making it ideal for family use or team projects in professional settings.
3. Expanded App Ecosystem
- Feature: A broader range of apps optimized for the Vision Pro, including productivity tools, games, and creative applications.
- Benefit: Users can access a variety of applications tailored to take advantage of AR capabilities, enhancing overall utility.
4. Gesture and Voice Control Improvements
- Feature: Enhanced gesture recognition and voice command capabilities for more intuitive navigation and interaction.
- Benefit: Makes it easier to control apps and content without needing handheld controllers, providing a more immersive experience.
5. Integration with Apple Ecosystem
- Feature: Deeper integration with other Apple devices, such as iPhones, iPads, and Macs, allowing for seamless sharing of content and continuity across devices.
- Benefit: Enhances user convenience by enabling synchronized experiences and easy access to files and applications.
6. Customizable User Interface
- Feature: A more customizable user interface that allows users to arrange their digital workspace according to their preferences.
- Benefit: Provides a personalized experience, making it easier for users to access frequently used apps and tools.
7. Improved Privacy Settings
- Feature: Enhanced privacy features that allow users to control data sharing and manage permissions more effectively.
- Benefit: Increases user confidence in using the device by ensuring better data protection.
Conclusion
These software enhancements to the Apple Vision Pro underscore Apple's commitment to creating a versatile and user-friendly AR experience, blending digital content seamlessly with the physical world while providing powerful tools for collaboration and personalization.
Read more
Which companies demonstrated the most significant improvements?
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
At CES 2025, several companies demonstrated significant improvements in AR glasses technology. Here are some of the standout companies and their advancements:

1. Microsoft
- Improvements: The HoloLens 3 showcased enhanced optics and a significantly wider field of view, improving user experience in mixed reality applications. The integration of better spatial mapping and cloud services for real-time collaboration marked a leap in enterprise usability.
2. Nreal
- Improvements: The Nreal Air emphasized a lighter design with upgraded display technology, offering better brightness and clarity. These enhancements aim to create more immersive experiences for gaming and entertainment, catering to a consumer audience.
3. Snap
- Improvements: The Snap Spectacles 4 introduced enhanced AR capabilities with a wider field of view and improved camera quality. These updates focus on content creation, appealing to social media users and creators.
4. Vuzix
- Improvements: The Vuzix Blade 2 featured a revamped design with longer battery life and augmented reality functionalities tailored for professional applications. This targeted approach to business use cases represents a significant step forward in AR for industry.
5. Apple
- Improvements: The updates to the Apple Vision Pro included performance enhancements and new software features that integrate seamlessly with Apple's ecosystem. This focus on user experience and ecosystem connectivity solidified Apple's position in the AR space.
Conclusion
These companies demonstrated the most significant advancements in AR glasses at CES 2025, focusing on improvements in design, functionality, and user experience. Their innovations reflect the growing demand for immersive and practical applications of AR technology in both consumer and enterprise markets.
Read more
At CES 2025, several companies demonstrated significant improvements in AR glasses technology. Here are some of the standout companies and their advancements:

1. Microsoft
- Improvements: The HoloLens 3 showcased enhanced optics and a significantly wider field of view, improving user experience in mixed reality applications. The integration of better spatial mapping and cloud services for real-time collaboration marked a leap in enterprise usability.
2. Nreal
- Improvements: The Nreal Air emphasized a lighter design with upgraded display technology, offering better brightness and clarity. These enhancements aim to create more immersive experiences for gaming and entertainment, catering to a consumer audience.
3. Snap
- Improvements: The Snap Spectacles 4 introduced enhanced AR capabilities with a wider field of view and improved camera quality. These updates focus on content creation, appealing to social media users and creators.
4. Vuzix
- Improvements: The Vuzix Blade 2 featured a revamped design with longer battery life and augmented reality functionalities tailored for professional applications. This targeted approach to business use cases represents a significant step forward in AR for industry.
5. Apple
- Improvements: The updates to the Apple Vision Pro included performance enhancements and new software features that integrate seamlessly with Apple's ecosystem. This focus on user experience and ecosystem connectivity solidified Apple's position in the AR space.
Conclusion
These companies demonstrated the most significant advancements in AR glasses at CES 2025, focusing on improvements in design, functionality, and user experience. Their innovations reflect the growing demand for immersive and practical applications of AR technology in both consumer and enterprise markets.

