
Electronics#ar #VR #AR Glasses #Augmented Reality #Virtual Reality #techtok #cftech
Use this section to provide a description of your blog./pages/blog
How does the Optical waveguide disappearance in technique?
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
The "optical waveguide disappearance technique" typically refers to methods used in optics and photonics to manipulate or conceal optical waveguides. While the term may not be widely recognized, it can relate to several concepts and applications. Here’s a general overview and possible contexts in which this technique might apply:
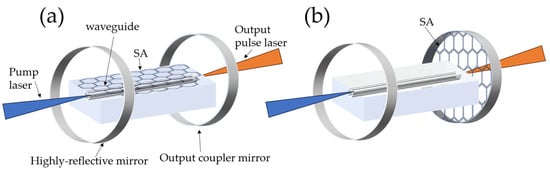
1. Optical Waveguide Basics
- Optical waveguides are structures that guide light, commonly used in fibers, integrated optics, and photonic circuits. They confine light to a specific path and can form the backbone of communication systems and sensors.
2. Disappearance Techniques
- Camouflage in Photonics: Techniques might be employed to make optical waveguides less visible or detectable. This can be crucial in applications like stealth technology or in devices where aesthetics matter.
- Integration with Materials: Using materials that match the refractive index of the waveguide to blend it into surrounding structures. This helps minimize reflections and visibility.
- Adaptive Optics: Implementing systems that dynamically adjust to environmental changes to minimize the visibility of waveguides in certain applications.
3. Applications
- Telecommunications: In fiber optics, ensuring minimal interference and subtle integration into environments.
- Sensors: Techniques to adapt sensors using optical waveguides for measuring environmental parameters without drawing attention.
- Consumer Electronics: Concealing waveguide structures within devices for aesthetic appeal or functional design.
4. New Materials and Techniques
- Metamaterials: Research into metamaterials could allow for the manipulation of light in ways that might render waveguides "invisible" under certain conditions.
- Nano-patterning: Advances in nanotechnology might also provide ways to create more efficient waveguides that blend seamlessly into their environments.
5. Future Directions
- The study of advanced optical materials and techniques will likely continue to explore ways to reduce visibility while enhancing performance in optical systems.
Conclusion
The optical waveguide disappearance technique encompasses various methods aimed at reducing the visibility of waveguides in applications where aesthetics, stealth, or integration are essential. As developments in materials science and optical engineering progress, we can expect innovations that will enhance the functionality and invisibility of optical waveguides.
Read more
The "optical waveguide disappearance technique" typically refers to methods used in optics and photonics to manipulate or conceal optical waveguides. While the term may not be widely recognized, it can relate to several concepts and applications. Here’s a general overview and possible contexts in which this technique might apply:

1. Optical Waveguide Basics
- Optical waveguides are structures that guide light, commonly used in fibers, integrated optics, and photonic circuits. They confine light to a specific path and can form the backbone of communication systems and sensors.
2. Disappearance Techniques
- Camouflage in Photonics: Techniques might be employed to make optical waveguides less visible or detectable. This can be crucial in applications like stealth technology or in devices where aesthetics matter.
- Integration with Materials: Using materials that match the refractive index of the waveguide to blend it into surrounding structures. This helps minimize reflections and visibility.
- Adaptive Optics: Implementing systems that dynamically adjust to environmental changes to minimize the visibility of waveguides in certain applications.
3. Applications
- Telecommunications: In fiber optics, ensuring minimal interference and subtle integration into environments.
- Sensors: Techniques to adapt sensors using optical waveguides for measuring environmental parameters without drawing attention.
- Consumer Electronics: Concealing waveguide structures within devices for aesthetic appeal or functional design.
4. New Materials and Techniques
- Metamaterials: Research into metamaterials could allow for the manipulation of light in ways that might render waveguides "invisible" under certain conditions.
- Nano-patterning: Advances in nanotechnology might also provide ways to create more efficient waveguides that blend seamlessly into their environments.
5. Future Directions
- The study of advanced optical materials and techniques will likely continue to explore ways to reduce visibility while enhancing performance in optical systems.
Conclusion
The optical waveguide disappearance technique encompasses various methods aimed at reducing the visibility of waveguides in applications where aesthetics, stealth, or integration are essential. As developments in materials science and optical engineering progress, we can expect innovations that will enhance the functionality and invisibility of optical waveguides.
Read more
Why is the tooling super important in AR glasses development?
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
Tooling is critically important in the development of AR (Augmented Reality) glasses for several reasons:

1. Precision and Quality
- Component Accuracy: Tooling ensures that each component of the AR glasses is manufactured with high precision, which is essential for optics and electronic functionalities.
- Consistent Quality: High-quality molds and tooling result in uniform parts, reducing defects and ensuring reliable performance.
2. Complexity Management
- Complex Geometries: AR glasses involve intricate designs, including housing for optics, sensors, and electronics. Well-designed tooling can address these complexities effectively.
- Customization: Tooling allows for customization of components based on user feedback or changing market demands.
3. Cost Efficiency
- Economies of Scale: Effective tooling enables mass production, reducing the cost per unit. This is essential for making the final product economically viable.
- Reduced Waste: Precision tooling minimizes material waste during production, lowering overall costs.
4. Speed to Market
- Rapid Prototyping: Advanced tooling allows for quicker iterations of prototypes. This speed can help teams test and refine designs more rapidly, ultimately accelerating time to market.
- Production Readiness: Well-prepared tooling ensures that once a design is finalized, production can begin without significant delays or rework.
5. Integration of Technology
- Incorporating Advanced Features: AR glasses often integrate various technologies such as cameras, sensors, and displays. Tooling facilitates the precise mounting and alignment of these technologies.
- Support for Electronic Components: Proper tooling ensures that electronic components fit correctly and function as intended, which is critical for performance.
6. Durability and Performance
- Handling Wear and Tear: High-quality tooling contributes to the strength and durability of components, ensuring they can withstand everyday use.
- Thermal Management: Tooling can address thermal expansion and cooling requirements, important for maintaining performance in compact devices.
7. Innovation and Differentiation
- Unique Aesthetic Designs: Effective tooling allows for innovative designs that can differentiate a product in a competitive market.
- New Functionalities: It enables the incorporation of new features that can set the product apart from competitors.
Conclusion
Tooling is foundational to developing AR glasses, impacting precision, cost, quality, and production speed. Investing in advanced tooling processes lays the groundwork for successful product development, ensuring that the AR glasses meet the high standards required for market acceptance and user satisfaction.
Read more
Tooling is critically important in the development of AR (Augmented Reality) glasses for several reasons:

1. Precision and Quality
- Component Accuracy: Tooling ensures that each component of the AR glasses is manufactured with high precision, which is essential for optics and electronic functionalities.
- Consistent Quality: High-quality molds and tooling result in uniform parts, reducing defects and ensuring reliable performance.
2. Complexity Management
- Complex Geometries: AR glasses involve intricate designs, including housing for optics, sensors, and electronics. Well-designed tooling can address these complexities effectively.
- Customization: Tooling allows for customization of components based on user feedback or changing market demands.
3. Cost Efficiency
- Economies of Scale: Effective tooling enables mass production, reducing the cost per unit. This is essential for making the final product economically viable.
- Reduced Waste: Precision tooling minimizes material waste during production, lowering overall costs.
4. Speed to Market
- Rapid Prototyping: Advanced tooling allows for quicker iterations of prototypes. This speed can help teams test and refine designs more rapidly, ultimately accelerating time to market.
- Production Readiness: Well-prepared tooling ensures that once a design is finalized, production can begin without significant delays or rework.
5. Integration of Technology
- Incorporating Advanced Features: AR glasses often integrate various technologies such as cameras, sensors, and displays. Tooling facilitates the precise mounting and alignment of these technologies.
- Support for Electronic Components: Proper tooling ensures that electronic components fit correctly and function as intended, which is critical for performance.
6. Durability and Performance
- Handling Wear and Tear: High-quality tooling contributes to the strength and durability of components, ensuring they can withstand everyday use.
- Thermal Management: Tooling can address thermal expansion and cooling requirements, important for maintaining performance in compact devices.
7. Innovation and Differentiation
- Unique Aesthetic Designs: Effective tooling allows for innovative designs that can differentiate a product in a competitive market.
- New Functionalities: It enables the incorporation of new features that can set the product apart from competitors.
Conclusion
Tooling is foundational to developing AR glasses, impacting precision, cost, quality, and production speed. Investing in advanced tooling processes lays the groundwork for successful product development, ensuring that the AR glasses meet the high standards required for market acceptance and user satisfaction.
Read more
What is the most costly aspect of developing AR Glasses?
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
Developing AR (Augmented Reality) glasses involves several cost factors. Here are the key components that contribute to the overall expense:

1. Research and Development (R&D)
- Initial R&D to explore new technologies, user experiences, and market potential.
- Prototyping and iterative testing to refine designs.

2. Hardware Development
- Optics: Developing high-quality displays, lenses, and waveguides.
- Sensors: Integration of cameras, depth sensors, and motion tracking devices.
- Processors: Developing or sourcing powerful CPUs and GPUs to support AR functionalities.
- Battery: Designing compact and efficient power solutions to ensure long usage times.
- Tooling cost: The Actual manufacturing of molds can range from$60,000 over $150,000 per mold, depending on material(steel vs aluminum) and complexity.
3. Software Development
- Developing the operating system or platform for the AR glasses.
- Creating applications, user interfaces, and user experiences (UX/UI).
- Incorporating AR software frameworks and SDKs (Software Development Kits).
4. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- Costs associated with sourcing materials, manufacturing components, and assembly.
- Quality control and testing to ensure reliability and performance.
- Establishing relationships with suppliers and manufacturers.
5. Intellectual Property and Licensing
- Costs for patents, licenses, or the use of third-party technologies or software.
- Legal fees associated with intellectual property protection.
6. Marketing and Distribution
- Creating marketing strategies to promote the product, including branding and advertising.
- Distribution logistics, including partnerships with retail or online sales channels.
7. Compliance and Certification
- Ensuring the product meets regulatory standards and certifications (e.g., safety, wireless communication).
8. Post-Launch Support
- Ongoing software updates, customer support, and warranty services.
- Collecting user feedback for improving future versions or models.
Summary
The total costs can range significantly, often reaching millions of dollars, depending on the technology, features, and scale of production. Companies must assess each of these factors meticulously to create a viable budget and plan for successful AR glasses development.
Read more
Developing AR (Augmented Reality) glasses involves several cost factors. Here are the key components that contribute to the overall expense:

1. Research and Development (R&D)
- Initial R&D to explore new technologies, user experiences, and market potential.
- Prototyping and iterative testing to refine designs.

2. Hardware Development
- Optics: Developing high-quality displays, lenses, and waveguides.
- Sensors: Integration of cameras, depth sensors, and motion tracking devices.
- Processors: Developing or sourcing powerful CPUs and GPUs to support AR functionalities.
- Battery: Designing compact and efficient power solutions to ensure long usage times.
- Tooling cost: The Actual manufacturing of molds can range from$60,000 over $150,000 per mold, depending on material(steel vs aluminum) and complexity.
3. Software Development
- Developing the operating system or platform for the AR glasses.
- Creating applications, user interfaces, and user experiences (UX/UI).
- Incorporating AR software frameworks and SDKs (Software Development Kits).
4. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- Costs associated with sourcing materials, manufacturing components, and assembly.
- Quality control and testing to ensure reliability and performance.
- Establishing relationships with suppliers and manufacturers.
5. Intellectual Property and Licensing
- Costs for patents, licenses, or the use of third-party technologies or software.
- Legal fees associated with intellectual property protection.
6. Marketing and Distribution
- Creating marketing strategies to promote the product, including branding and advertising.
- Distribution logistics, including partnerships with retail or online sales channels.
7. Compliance and Certification
- Ensuring the product meets regulatory standards and certifications (e.g., safety, wireless communication).
8. Post-Launch Support
- Ongoing software updates, customer support, and warranty services.
- Collecting user feedback for improving future versions or models.
Summary
The total costs can range significantly, often reaching millions of dollars, depending on the technology, features, and scale of production. Companies must assess each of these factors meticulously to create a viable budget and plan for successful AR glasses development.
Read more
What do you have to know about the Hardware specification parameters of AR surgical smart glasses?
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
When evaluating the hardware specifications of AR surgical smart glasses, it's essential to consider several key parameters that directly impact their functionality, usability, and performance in a surgical context. Here’s what you need to know:

1. Display Technology
- Type: Common technologies include OLED and MicroLED, which offer high contrast and brightness.
- Resolution: A minimum of 1080p is typical, but higher resolutions (4K or more) are desirable for detailed imaging.
- Field of View (FOV): Ideally, it ranges from 30° to 100°; a wider FOV enhances immersion and usability.
- Brightness: Generally between 500 and 2000 nits, essential for visibility in brightly lit surgical environments.
- Contrast Ratio: Higher ratios (e.g., 10000:1) provide clearer images, especially for distinguishing fine details.
2. Processing Power
- Processor: Look for high-performance mobile processors, often based on ARM architecture, to handle complex tasks and real-time data processing.
- RAM: Typically between 4GB and 8GB, this enables smooth multitasking and efficient handling of applications.
- Storage: Ranges from 32GB to 256GB, with the option for expandable storage (often via microSD cards).
3. Sensors
- Cameras: High-definition front-facing cameras (1080p or higher) for capturing and streaming surgical procedures; depth sensors for 3D mapping.
- IMU: The inclusion of inertial measurement units (accelerometers and gyroscopes) enhances spatial awareness and tracking.
- Additional Sensors: Environmental sensors (temperature, humidity) may be included for specific applications.
4. Connectivity
- Wireless: Support for modern standards like Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.0 for fast data transfer and connectivity with other devices.
- Wired: USB-C or other connectors for charging and data transfer.
5. Audio System
- Microphone: Noise-canceling microphone arrays for clear voice capture in noisy surgical environments.
- Speakers: High-quality stereo output for audio feedback or communication.
6. Power and Battery
- Battery Type: Typically rechargeable lithium-ion; consider battery life for prolonged use during surgeries.
- Battery Life: Usually between 4 and 8 hours, depending on usage; fast-charging capabilities can be beneficial for quick turnaround.
- Charging Time: Generally, around 2 to 3 hours for a full charge.
7. Physical Characteristics
- Weight: Aiming for 200 to 400 grams helps ensure comfort during long procedures.
- Material: Durable yet lightweight materials (like polycarbonate or aluminum) are preferred for wearability and robustness.
- IP Rating: Look for an IP rating (such as IP65) to ensure dust and water resistance, critical for surgical settings.
8. Additional Features
- Voice Recognition: Essential for hands-free operation; aids surgeons in executing commands without manual interaction.
- Gesture Control: Allows for touchless interaction, which can be crucial in sterile environments.
- Cloud Integration: Facilitates data storage and processing in the cloud, enabling remote access to information.
Conclusion
Grasping the significance of hardware specifications is essential when selecting augmented reality (AR) surgical smart glasses that cater to the requirements of contemporary surgical practices. A thorough evaluation of each parameter in relation to specific surgical needs can enhance overall efficiency and improve patient care outcomes. It is important to ensure that these specifications correspond with the intended applications, allowing for the selection of the most suitable device for your clinical setting.
Read more
When evaluating the hardware specifications of AR surgical smart glasses, it's essential to consider several key parameters that directly impact their functionality, usability, and performance in a surgical context. Here’s what you need to know:

1. Display Technology
- Type: Common technologies include OLED and MicroLED, which offer high contrast and brightness.
- Resolution: A minimum of 1080p is typical, but higher resolutions (4K or more) are desirable for detailed imaging.
- Field of View (FOV): Ideally, it ranges from 30° to 100°; a wider FOV enhances immersion and usability.
- Brightness: Generally between 500 and 2000 nits, essential for visibility in brightly lit surgical environments.
- Contrast Ratio: Higher ratios (e.g., 10000:1) provide clearer images, especially for distinguishing fine details.
2. Processing Power
- Processor: Look for high-performance mobile processors, often based on ARM architecture, to handle complex tasks and real-time data processing.
- RAM: Typically between 4GB and 8GB, this enables smooth multitasking and efficient handling of applications.
- Storage: Ranges from 32GB to 256GB, with the option for expandable storage (often via microSD cards).
3. Sensors
- Cameras: High-definition front-facing cameras (1080p or higher) for capturing and streaming surgical procedures; depth sensors for 3D mapping.
- IMU: The inclusion of inertial measurement units (accelerometers and gyroscopes) enhances spatial awareness and tracking.
- Additional Sensors: Environmental sensors (temperature, humidity) may be included for specific applications.
4. Connectivity
- Wireless: Support for modern standards like Wi-Fi 6 and Bluetooth 5.0 for fast data transfer and connectivity with other devices.
- Wired: USB-C or other connectors for charging and data transfer.
5. Audio System
- Microphone: Noise-canceling microphone arrays for clear voice capture in noisy surgical environments.
- Speakers: High-quality stereo output for audio feedback or communication.
6. Power and Battery
- Battery Type: Typically rechargeable lithium-ion; consider battery life for prolonged use during surgeries.
- Battery Life: Usually between 4 and 8 hours, depending on usage; fast-charging capabilities can be beneficial for quick turnaround.
- Charging Time: Generally, around 2 to 3 hours for a full charge.
7. Physical Characteristics
- Weight: Aiming for 200 to 400 grams helps ensure comfort during long procedures.
- Material: Durable yet lightweight materials (like polycarbonate or aluminum) are preferred for wearability and robustness.
- IP Rating: Look for an IP rating (such as IP65) to ensure dust and water resistance, critical for surgical settings.
8. Additional Features
- Voice Recognition: Essential for hands-free operation; aids surgeons in executing commands without manual interaction.
- Gesture Control: Allows for touchless interaction, which can be crucial in sterile environments.
- Cloud Integration: Facilitates data storage and processing in the cloud, enabling remote access to information.
Conclusion
Grasping the significance of hardware specifications is essential when selecting augmented reality (AR) surgical smart glasses that cater to the requirements of contemporary surgical practices. A thorough evaluation of each parameter in relation to specific surgical needs can enhance overall efficiency and improve patient care outcomes. It is important to ensure that these specifications correspond with the intended applications, allowing for the selection of the most suitable device for your clinical setting.
Read more
AI Smart Glasses Market: 5 Trends Reshaping Reality by 2026
Posted by Technology Co., Ltd Shenzhen Mshilor
Here are five key trends that will reshape the AI smart glasses market by 2026 — concise, evidence‑based, and focused on how each trend affects product design, go‑to‑market strategy, and user adoption.

- Miniaturized, Lower‑Power AI on Device (Edge AI)
- What’s changing: Advances in low‑power AI chips (NPU/DPUs), more efficient models (quantization, pruning, tiny‑transformers), and improved sensor fusion allow meaningful on‑device inference (speech, vision, AR tracking) without constant cloud connectivity.
- Impact on product: Sleeker, lighter frames with longer battery life; reduced latency for features like real‑time translation, gesture recognition, and contextual overlays.
- GTM/ops implication: Differentiation moves from cloud subscriptions to device capabilities and privacy advantages; reduced connectivity lowers operating costs and expands addressable markets (offline/low‑bandwidth regions).
- Risk/constraint: On‑device models remain capacity‑constrained — advanced vision tasks may still need hybrid cloud assistance for heavy computation.
- Hybrid Cloud–Edge Architectures and Adaptive Workflows
- What’s changing: Products will increasingly use a hybrid approach — lightweight inference on device for latency‑sensitive tasks, with periodic cloud offload for heavy model updates, multi‑user AR scenes, large‑scale mapping, or personalization.
- Impact on product: Seamless UX that balances responsiveness and capability (e.g., local keyword spotting + cloud NLP for complex queries). Devices will include smarter sync/update mechanisms and configurable privacy controls.
- GTM/ops implication: Subscription tiers and service bundles (edge‑only, hybrid, enterprise cloud) become key revenue levers. Partnerships with cloud providers and telecoms (for MEC) will shape deployment.
- Risk/constraint: Network variability and cost (data, roaming) can complicate pricing and perceived value; enterprises will demand SLAs and on‑premise options.
- Contextual, Multimodal Interaction and True Hands‑Free UX
- What’s changing: Advances in multimodal models combine audio, gaze, gesture, and environment sensing to deliver contextually appropriate information and actions — voice + glance triggers, predictive suggestions, and natural language UI layered over the real world.
- Impact on product: New sensors (eye‑tracking, IMU improvements, bone‑conduction audio), better bone‑conduction/near‑ear speakers, and refined ergonomics to support continuous use. UI shifts from static overlays to contextual, ephemeral information.
- GTM/ops implication: Design and HCI become major competitive differentiators; focus on real‑world workflows (field service, healthcare, logistics) yields quicker enterprise adoption than pure consumer markets.
- Risk/constraint: UX complexity, accidental triggers, and privacy concerns (who’s being recorded/observed) require careful policy, fine‑grained controls, and strong edge privacy claims.
- Verticalization — Enterprise First, High‑Value Use Cases
- What’s changing: While consumer AR remains aspirational, enterprises (manufacturing, warehousing, healthcare, field service, military) will drive near‑term revenue with concrete ROI use cases: remote expert assistance, hands‑free workflows, AR instructions, safety overlays.
- Impact on product: Ruggedized models, longer warranties, integrated enterprise software, device management (MDM), and industry‑specific integrations (ERP, EHR, PLM).
- GTM/ops implication: Sales move toward channel/solution partners, system integrators, and subscription/managed‑service models. Proof‑of‑value pilots and outcome‑based contracting accelerate adoption.
- Risk/constraint: Sales cycles are longer, customization demands are higher, and support/maintenance needs raise the total cost of ownership considerations.
- Privacy, Regulation, and Social Acceptability Drive Design & Policy
- What’s changing: Growing concerns over facial recognition, continuous recording, and AR overlays will prompt stricter regulation and social pushback; jurisdictional privacy laws and public norms will shape which features are viable in which markets.
- Impact on product: Hardware and software controls (visible recording indicators, physical camera shutters, on‑device data minimization, audit logs), fine‑grained consent flows, and certification/labels for privacy‑preserving designs.
- GTM/ops implication: Compliance becomes a sales enabler—privacy certifications, enterprise SLAs, and transparent data policies will be required for public and B2B deployments. Marketing must address social acceptability (opt‑in experiences, opt‑out zones).
- Risk/constraint: Regulatory divergence across regions increases complexity for global rollouts; overly restrictive rules could limit some AR features.
Strategic implications for companies and investors
- Focus on hybrid hardware + software stacks: device differentiation (battery, comfort, on‑device AI) plus vertically targeted software suites will win near term.
- Build ecosystem and partnerships early: cloud providers (MEC), telcos, enterprise ISVs, SI partners, and standards bodies (privacy, AR UX) matter as much as component suppliers.
- Emphasize privacy and trust as selling points: on‑device inference and transparent controls create a competitive advantage and reduce legal/regulatory risk.
- Plan for phased markets: prioritize enterprise pilots with measurable ROI, then expand consumer experiences where social norms and battery/price constraints are favorable.
- Prepare flexible monetization: device sales + SaaS/subscriptions for cloud features, enterprise support contracts, and feature bundles (offline vs hybrid) to maximize AR license opportunities.
Read more
Here are five key trends that will reshape the AI smart glasses market by 2026 — concise, evidence‑based, and focused on how each trend affects product design, go‑to‑market strategy, and user adoption.

- Miniaturized, Lower‑Power AI on Device (Edge AI)
- What’s changing: Advances in low‑power AI chips (NPU/DPUs), more efficient models (quantization, pruning, tiny‑transformers), and improved sensor fusion allow meaningful on‑device inference (speech, vision, AR tracking) without constant cloud connectivity.
- Impact on product: Sleeker, lighter frames with longer battery life; reduced latency for features like real‑time translation, gesture recognition, and contextual overlays.
- GTM/ops implication: Differentiation moves from cloud subscriptions to device capabilities and privacy advantages; reduced connectivity lowers operating costs and expands addressable markets (offline/low‑bandwidth regions).
- Risk/constraint: On‑device models remain capacity‑constrained — advanced vision tasks may still need hybrid cloud assistance for heavy computation.
- Hybrid Cloud–Edge Architectures and Adaptive Workflows
- What’s changing: Products will increasingly use a hybrid approach — lightweight inference on device for latency‑sensitive tasks, with periodic cloud offload for heavy model updates, multi‑user AR scenes, large‑scale mapping, or personalization.
- Impact on product: Seamless UX that balances responsiveness and capability (e.g., local keyword spotting + cloud NLP for complex queries). Devices will include smarter sync/update mechanisms and configurable privacy controls.
- GTM/ops implication: Subscription tiers and service bundles (edge‑only, hybrid, enterprise cloud) become key revenue levers. Partnerships with cloud providers and telecoms (for MEC) will shape deployment.
- Risk/constraint: Network variability and cost (data, roaming) can complicate pricing and perceived value; enterprises will demand SLAs and on‑premise options.
- Contextual, Multimodal Interaction and True Hands‑Free UX
- What’s changing: Advances in multimodal models combine audio, gaze, gesture, and environment sensing to deliver contextually appropriate information and actions — voice + glance triggers, predictive suggestions, and natural language UI layered over the real world.
- Impact on product: New sensors (eye‑tracking, IMU improvements, bone‑conduction audio), better bone‑conduction/near‑ear speakers, and refined ergonomics to support continuous use. UI shifts from static overlays to contextual, ephemeral information.
- GTM/ops implication: Design and HCI become major competitive differentiators; focus on real‑world workflows (field service, healthcare, logistics) yields quicker enterprise adoption than pure consumer markets.
- Risk/constraint: UX complexity, accidental triggers, and privacy concerns (who’s being recorded/observed) require careful policy, fine‑grained controls, and strong edge privacy claims.
- Verticalization — Enterprise First, High‑Value Use Cases
- What’s changing: While consumer AR remains aspirational, enterprises (manufacturing, warehousing, healthcare, field service, military) will drive near‑term revenue with concrete ROI use cases: remote expert assistance, hands‑free workflows, AR instructions, safety overlays.
- Impact on product: Ruggedized models, longer warranties, integrated enterprise software, device management (MDM), and industry‑specific integrations (ERP, EHR, PLM).
- GTM/ops implication: Sales move toward channel/solution partners, system integrators, and subscription/managed‑service models. Proof‑of‑value pilots and outcome‑based contracting accelerate adoption.
- Risk/constraint: Sales cycles are longer, customization demands are higher, and support/maintenance needs raise the total cost of ownership considerations.
- Privacy, Regulation, and Social Acceptability Drive Design & Policy
- What’s changing: Growing concerns over facial recognition, continuous recording, and AR overlays will prompt stricter regulation and social pushback; jurisdictional privacy laws and public norms will shape which features are viable in which markets.
- Impact on product: Hardware and software controls (visible recording indicators, physical camera shutters, on‑device data minimization, audit logs), fine‑grained consent flows, and certification/labels for privacy‑preserving designs.
- GTM/ops implication: Compliance becomes a sales enabler—privacy certifications, enterprise SLAs, and transparent data policies will be required for public and B2B deployments. Marketing must address social acceptability (opt‑in experiences, opt‑out zones).
- Risk/constraint: Regulatory divergence across regions increases complexity for global rollouts; overly restrictive rules could limit some AR features.
Strategic implications for companies and investors
- Focus on hybrid hardware + software stacks: device differentiation (battery, comfort, on‑device AI) plus vertically targeted software suites will win near term.
- Build ecosystem and partnerships early: cloud providers (MEC), telcos, enterprise ISVs, SI partners, and standards bodies (privacy, AR UX) matter as much as component suppliers.
- Emphasize privacy and trust as selling points: on‑device inference and transparent controls create a competitive advantage and reduce legal/regulatory risk.
- Plan for phased markets: prioritize enterprise pilots with measurable ROI, then expand consumer experiences where social norms and battery/price constraints are favorable.
- Prepare flexible monetization: device sales + SaaS/subscriptions for cloud features, enterprise support contracts, and feature bundles (offline vs hybrid) to maximize AR license opportunities.

